
Cases of highly contagious whooping cough or pertussis have witnessed a fourfold rise this season across the USA, compared to last year, which has raised concerns among parents and health authorities. Whooping cough, which commonly affects children, starts with a mild illness with symptoms resembling common cold like runny or stuffy nose, low-grade fever, mild and occasional coughing, but as the days go by, it can turn more severe, putting certain kids at risk of life-threatening complications.
Whooping cough is particularly worrying because children affected by it gasp for air in between the coughing fits, letting out a sound which is called whoop. The airways of infants are small, which means they struggle to breathe when they are overwhelmed with coughing fits.
How whooping cough symptoms progress

In early stages, whooping cough symptoms are mild and range from a runny nose, mild fever, to sore throat. However, the disease can worsen as uncontrollable coughing fits, often followed by a ‘whoop’ start after a week or two of the illness.
It is especially distressing for infants. While they do not make ‘whoop’ sound, they struggle to breathe or turn blue during coughing fits for around 20 seconds. The coughing fits can be intense, causing difficulty in breathing, vomiting, and exhaustion.
With the right treatment, the severity of the symptoms is reduced, but if not treated in time, complications such as pneumonia, seizures, and even death can occur.
What happens in advanced states of whooping cough

According to CDC, around 1 in 3 babies younger than 1 year old who get this disease may develop life-threatening symptoms that require hospitalisation. Whooping cough is especially troublesome for infants who find themselves at serious threats of complications.
Babies younger than 1 year old who are treated in the hospital can have apnea, pneumonia or lung infection, or around 2% of infants can suffer from convulsions or violent, uncontrollable shaking. Even more rarely, encephalopathy, a brain disease, can occur in 0.6% of the babies. It is estimated that around 1% of babies could die from complications of whooping cough.
Whooping cough is treated with the help of antibiotics that can help reduce the severity of symptoms and in preventing the spread of the infection if taken early.
In severe cases, particularly in infants, hospitalization may be necessary to provide supportive care, including oxygen and fluids.
Precautions to take
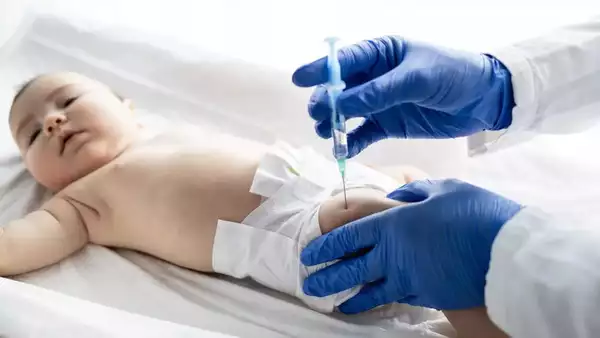
Pregnant mothers are advised to take the whooping cough vaccine between 20 and 32 weeks to protect their newborns from infection.
Infants must receive the vaccine as part of the routine childhood vaccination schedule. The diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (DTaP) vaccine protects against diphtheria, tetanus (lockjaw), and pertussis (whooping cough) and is given at given as a series of 5 injections, usually administered at 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, 15–18 months, and 4–6 years of age.
Tdap vaccine (booster) should be given between 11-12 years of age and to older teens and adults who haven’t yet had a booster with pertussis coverage. Then, Td (tetanus and diphtheria) boosters may be given once every ten years.
Covid-19: Why wearing a mask is important?





