Cases of highly contagious whooping cough or pertussis have witnessed a fourfold rise this season across the USA, compared to last year, which has raised concerns among parents and health authorities. Whooping cough, which commonly affects children, starts with a mild illness with symptoms resembling common cold like runny or stuffy nose, low-grade fever, mild and occasional coughing, but as the days go by, it can turn more severe, putting certain kids at risk of life-threatening complications.
Whooping cough is particularly worrying because children affected by it gasp for air in between the coughing fits, letting out a sound which is called whoop. The airways of infants are small, which means they struggle to breathe when they are overwhelmed with coughing fits.
How whooping cough symptoms progress

In early stages, whooping cough symptoms are mild and range from a runny nose, mild fever, to sore throat. However, the disease can worsen as uncontrollable coughing fits, often followed by a ‘whoop’ start after a week or two of the illness.
It is especially distressing for infants. While they do not make ‘whoop’ sound, they struggle to breathe or turn blue during coughing fits for around 20 seconds. The coughing fits can be intense, causing difficulty in breathing, vomiting, and exhaustion.
With the right treatment, the severity of the symptoms is reduced, but if not treated in time, complications such as pneumonia, seizures, and even death can occur.
What happens in advanced states of whooping cough

According to CDC, around 1 in 3 babies younger than 1 year old who get this disease may develop life-threatening symptoms that require hospitalisation. Whooping cough is especially troublesome for infants who find themselves at serious threats of complications.
Babies younger than 1 year old who are treated in the hospital can have apnea, pneumonia or lung infection, or around 2% of infants can suffer from convulsions or violent, uncontrollable shaking. Even more rarely, encephalopathy, a brain disease, can occur in 0.6% of the babies. It is estimated that around 1% of babies could die from complications of whooping cough.
Whooping cough is treated with the help of antibiotics that can help reduce the severity of symptoms and in preventing the spread of the infection if taken early.
In severe cases, particularly in infants, hospitalization may be necessary to provide supportive care, including oxygen and fluids.
Precautions to take
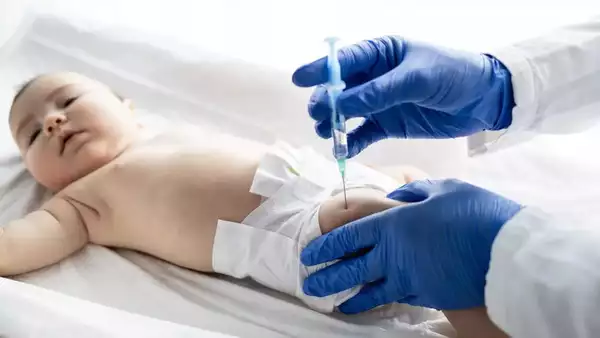
Pregnant mothers are advised to take the whooping cough vaccine between 20 and 32 weeks to protect their newborns from infection.
Infants must receive the vaccine as part of the routine childhood vaccination schedule. The diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (DTaP) vaccine protects against diphtheria, tetanus (lockjaw), and pertussis (whooping cough) and is given at given as a series of 5 injections, usually administered at 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, 15–18 months, and 4–6 years of age.
Tdap vaccine (booster) should be given between 11-12 years of age and to older teens and adults who haven’t yet had a booster with pertussis coverage. Then, Td (tetanus and diphtheria) boosters may be given once every ten years.
Covid-19: Why wearing a mask is important?
Antibiotics are antimicrobial substances and are medications that treat and prevent bacterial infections by killing or stopping the growth of bacteria. While antibiotics are effective in treating many bacterial infections, the misuse or wrong use of antibiotics can lead to health issues, including antibiotic resistance. Dr Anita Mathew, Director-Internal Medicine & Consultant-Infectious Diseases, Fortis Hospital, Mulund, shares her insights.
“Antibiotics are a class of drugs that was discovered by Sir Alexander Fleming and the first substance discovered was Penicillin. The discovery of this molecule was thought to be the end of all infections. However, Dr Fleming expressed concern that bacteria could develop resistance to Penicillin, leading to the emergence of ‘Penicillin-resistant’ strains. While he hoped this issue could be avoided, it has since become a significant challenge in medicine across the world,” says Dr Mathew.
Since the introduction of penicillin, the number of bacteria resistant to it, as well as to newer classes of antibiotics, has significantly increased, Dr Matthew shares. She adds, “We now face a troubling situation characterised by lack of research into new antibiotic classes. If antibiotic misuse continues, we are likely to see rising rates of mortality and morbidity due to drug-resistant infections.”
The doctor insists that the public plays a crucial role in mitigating the risk of drug-resistant bacteria within the community.
Antibiotic Resistance: Get Your Facts Right
Dr Anita Matthew shares a few facts one must bear in mind when it comes to antibiotics. Read on:
1. Antibiotics act only on bacteria. They have no role in viral infection. Taking an antibiotic for example a flu-like symptom, does not reduce the duration and severity of viral infection.
2. There is nothing like ‘not completing the course of antibiotics will lead to resistance’. If you happen to take an antibiotic for a viral infection, then stopping that earlier will be beneficial. And to take an appropriate dose of antibiotic for an appropriate duration in a bacterial infection does not lead to resistance.
3. Antibiotics should be used only when it is felt necessary by your physician. The idea of wanting to get better as quickly as possible sometimes puts a lot of pressure on doctors, which in turn may cause inappropriate drug prescriptions. So, both doctors and patients have to be patient and judicious.
4. Keeping antibiotics, which were left over from the previous prescription, and reusing them even when they aren’t appropriate for the current illness increases the risk of drug resistance.
5. Our bodies don’t become resistant to antibiotics. It’s the bacteria which develops resistance.
6. Hospitals don’t breed resistant bugs. There is an overwhelming use of antibiotics in farm produce and livestock, both of these are major contributory factors in drug-resistant bacteria.
7. Use of low-quality antibiotics, which may not have the requisite number of active molecules, and dumping of the pharma industrial waste also increases the risk of antibiotic resistance.